When was the last time you reviewed your implementation of hashCode and equals in your Java classes? These two methods are fundamental, yet often overlooked, pillars of Java development. They determine how objects behave in collections, influence performance, and can be the silent culprits behind those elusive bugs.
In microservices architectures, where data consistency and identity are critical, a robust understanding of hashCode and equals is non-negotiable. A poorly implemented equals can break business logic, while an inconsistent hashCode can wreak havoc in hash-based collections like HashSet and HashMap.
Here are a few key points to remember:
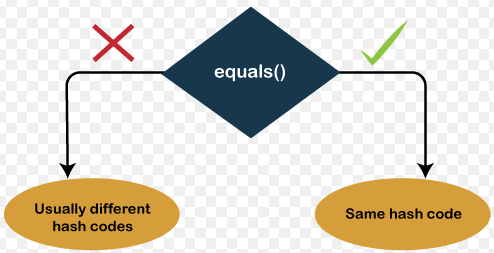
- Consistency is key: If two objects are equal according to
equals, they must have the samehashCode. - Performance matters: Efficient implementations can significantly improve collection operations.
- Null safety: Always handle nulls gracefully to avoid
NullPointerExceptions. - Symmetry and transitivity: Your
equalsmethod must be symmetric and transitive to avoid unpredictable behavior.
I’m curious:
- Have you ever faced a tricky bug because of a bad
hashCodeorequalsimplementation? - Do you use any tools or libraries to help generate these methods?
- What best practices do you follow to ensure correctness?
Let’s share experiences and tips! Drop your thoughts, stories, or questions in the comments.
#Java #SpringBoot #Backend #Microservices #CleanCode #SoftwareEngineering #HashCode #Equals #Programming #TechCommunity #BestPractices